
Our Procedures
We focus inComprehensive Women’s Health Care,Laparoscopic Surgery, Endoscopic Surgery, Minimally Invasive Surgery

Laparoscopic Hysterectomy (LH)
Many of the women in need for a hysterectomy are candidates for LH .It is an alternative to the total abdominal hysterectomy which requires a 5-7 inch incision. In the united states, about 70% of the hysterectomies are performed as total abdominal hysterectomies. Most of these can be accomplished laparoscopically when performed by an experienced laparoscopic surgeon.

Supracervical Hysterectomy
In the absence of cervical pathology, the body of the uterus can be removed leaving the healthy cervix in place. This procedure requires less surgery than the hysterectomy that includes removal of the cervix (called Total Hysterectomy).
In addition, some scientists believe that preserving the cervix may help maintain a normal sexual function and normal pelvic support since the nerves and blood supply to the cervix and upper vagina are not interrupted.

Reconstructive Pelvic Surgery
Pelvic organ prolapse refers to a protrusion of a mass through the vagina. The protruding mass can be the uterus (uterine prolapse), the bladder (cystocele),the urethra (urethrocele),the rectum (rectocele), the vaginal apex (vaginal vault prolapse), or bowel (enterocele). Usually it is a combination of some or all these conditions. This creates pelvic pressure, pain , difficulty voiding or controlling the bladder, or difficulty in having bowel movements. The protruding mass ,if neglected, can bleed, get ulcerated or get infected.

Urinary Incontinence Surgery
The involuntary leakage of urine is abnormal at any age. There are several types of urinary incontinence, but the most common among women is called "stress incontinence" which refers to loss of urine when straining (e.g. laughing , coughing, sneezing, etc). There are non-surgical methods for treatment of this condition including pelvic muscle exercises, medications and hormonal replacement if indicated. However, if conservative therapy does not yield satisfactory results, then surgery could be the right option. The procedures that are commonly used for this condition are:
- Suburethral sling procedure in which a mesh strip is placed under and around the sides of the urethra to stabilize it. This can be accomplished in a minimally invasive procedure called TVT (Tension Free Vaginal Tape) which requires two small band aid incisions just above the pubic bone and a small incision under the urethra. When other laparoscopic pelvic procedures are necessary, the sling procedure can be done through the laparoscope.
- Laparoscopic Burch procedure: In this procedure, sutures are placed on the sides of the urethra to stabilize it. This is done laparoscopically and does not require the use of a mesh.Preoperative evaluation determines which procedure would be more appropriate. Sometimes, the patient has other pelvic prolapse conditions that must be corrected at the same time in order to achieve best results. In other words, surgery for urinary incontinence can be one part of a more comprehensive pelvic reconstructive procedure. (see laparoscopic pelvic reconstructive surgery for prolapse).

Endometriosis Surgery
- Endometriosis refers to a condition in which glands similar to those lining the uterine cavity (endometrium) are present inside the pelvis and abdomen or less often in other parts of the body.
- The usual symptoms include cyclic or persistent pelvic pain , painful intercourse, and painful heavy menses.
In addition ,there is an association between endometriosis and infertility.
- Treatment of endometriosis can be medical with hormones, surgical by resection of the endometriosis tissue from the surrounding normal tissue. Sometimes, endometriosis is very extensive, involving the ovaries, tubes, the rectum ,the culdesac (the pouch between the uterus and rectum) or the bladder requiring extensive resection .It is vital to have an experienced surgeon perform the surgery when dealing with extensive endometriosis. Medical treatment frequently helps with the symptoms but most of the times does not eradicate the disease. Symptoms may recur after discontinuation of medical treatment.

Fibroid Surgery
A fibroid is a benign tumor of the uterine wall, it can be single or multiple, small or large and can involve any part of the uterus. About 20% of women over the age 35 have fibroid tumors. The symptoms include pelvic pain and heavy menses. During pregnancy, fibroids tend to grow in size and may lead to complications such as spontaneous abortion or preterm labor.
When symptomatic and small, medical therapy may control the symptoms. Otherwise, fibroids can be removed by a procedure called myomectomy in which the fibroid is shelled out of the uterine wall . Depending on the size, number, and location of the fibroids, the surgeon will decide on how to remove the fibroids ( laparoscopically or open). For patients who completed their families, hysterectomy is usually an option.
Another procedure for fibroid treatment involves cauterization of the fibroid using needle electrodes, this makes it shrink and ultimately less symptomatic.
A new procedure called fibroid embolization performed by invasive radiologists (not gynecologists) seems to be promising. During the procedure, the artery feeding the fibroid is occluded with a synthetic material. The technique is similar to some extent to cardiac cathetarization. This procedure makes the fibroid shrink and improves the symptoms.

Ovarian and Tubal Surgery
Surgery on the ovaries and the fallopian tubes is sometimes necessary.The usual indications include ovarian cysts, tubal ectopic pregnancy, endometriosis, infertility, and adhesions. In the presence of pelvic adhesions, the surgery can be difficult. Meticulous dissection may become necessary to guarantee removal of all the ovarian cyst wall or all of the ovary or tube when indicated. Also, the ureter which runs close to the ovary may need to be identified and dissected out to prevent its injury during the course of surgery.
Following the laparoscopic procedure, the patient is usually allowed to go home the same day.

Laparoscopic Surgery for Gynecologic Cancers
In selected cases of gynecologic malignancies (cancer), the surgical procedure can be performed via the laparoscope including the pelvic lymph node dissection and omentectomy.
- Laparoscopic pelvic lymphnode dissection
- Laparoscopic para- aortic lymphnode dissection with audio
- Laparoscopic Omentectomy

Aesthetic Genital Plastic Surgery
(beautification) of the External Genitalia
- Labial reduction: In some women, the labia minora can be larger than what a woman considers aesthetically acceptable and on occasions, it can cause discomfort and irritation of the skin. In such situations, surgical labial reduction can be achieved in a certain way that does not affect the natural look, shape or color of the skin. backpack bag laptop.
- Fat transfer: As the body ages, the skin of the external genitalia loses its elasticity and becomes redundant. To achieve a fuller and more youthful appearance, fat removed from other parts of the body , such as the abdominal wall, is injected under the skin of the external genitalia.

Hysteroscopy
- This is visualization of the inside of the uterus (the endometrial cavity) to help diagnose and treat certain conditions such as submucus fibroids and polyps that protrude in to the uterine cavity. These can cause abnormal bleeding and pain.
- This is accomplished using a telescope called a hysteroscope. It is introduced through the vagina and cervix in to the uterine cavity (no incisions needed) The uterine cavity is kept open using saline or other types of fluids. If a fibroid or a polyp is present, it can be excised at the same session if appropriate.















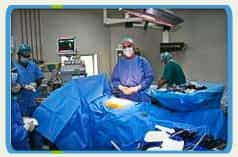
 Dr. Badran performs his minimally invasive laparoscopic and hysteroscopic procedures in the best private hospitals in Amman.
Dr. Badran performs his minimally invasive laparoscopic and hysteroscopic procedures in the best private hospitals in Amman. the Dead Sea, visit incredible ruins yet experience the ultimate in luxurious accommodations and dining in one of the most beautiful desert kingdom's in the world. Jordan continues to be a leader in organ transplant, cardiac and laparoscopic surgical procedures as well as cancer treatments in the world. Jordan is also an ultimate tourist destination, and has been for hundreds of years.
the Dead Sea, visit incredible ruins yet experience the ultimate in luxurious accommodations and dining in one of the most beautiful desert kingdom's in the world. Jordan continues to be a leader in organ transplant, cardiac and laparoscopic surgical procedures as well as cancer treatments in the world. Jordan is also an ultimate tourist destination, and has been for hundreds of years.
 All the hospitals are State of the art facilities and provide the highest standardof medical care.
All the hospitals are State of the art facilities and provide the highest standardof medical care.








Share this listing