Stem Cell Research Provides Promise for Future Treatments
Overview
Stem cell research has been around for decades, but not to the extent it is today. In early 2009, President Obama signed an Executive Order that will lift many of the restrictions on stem cell research in the second decade of the 21st century.
Stem cell research involves so much more than embryonic stem cell research and utilizes adult stem cells, umbilical stem cells and placenta stem cells in the search for treatments and cures of many disease processes that kill thousands of people every day.
Focus on Auto-Immune Diseases
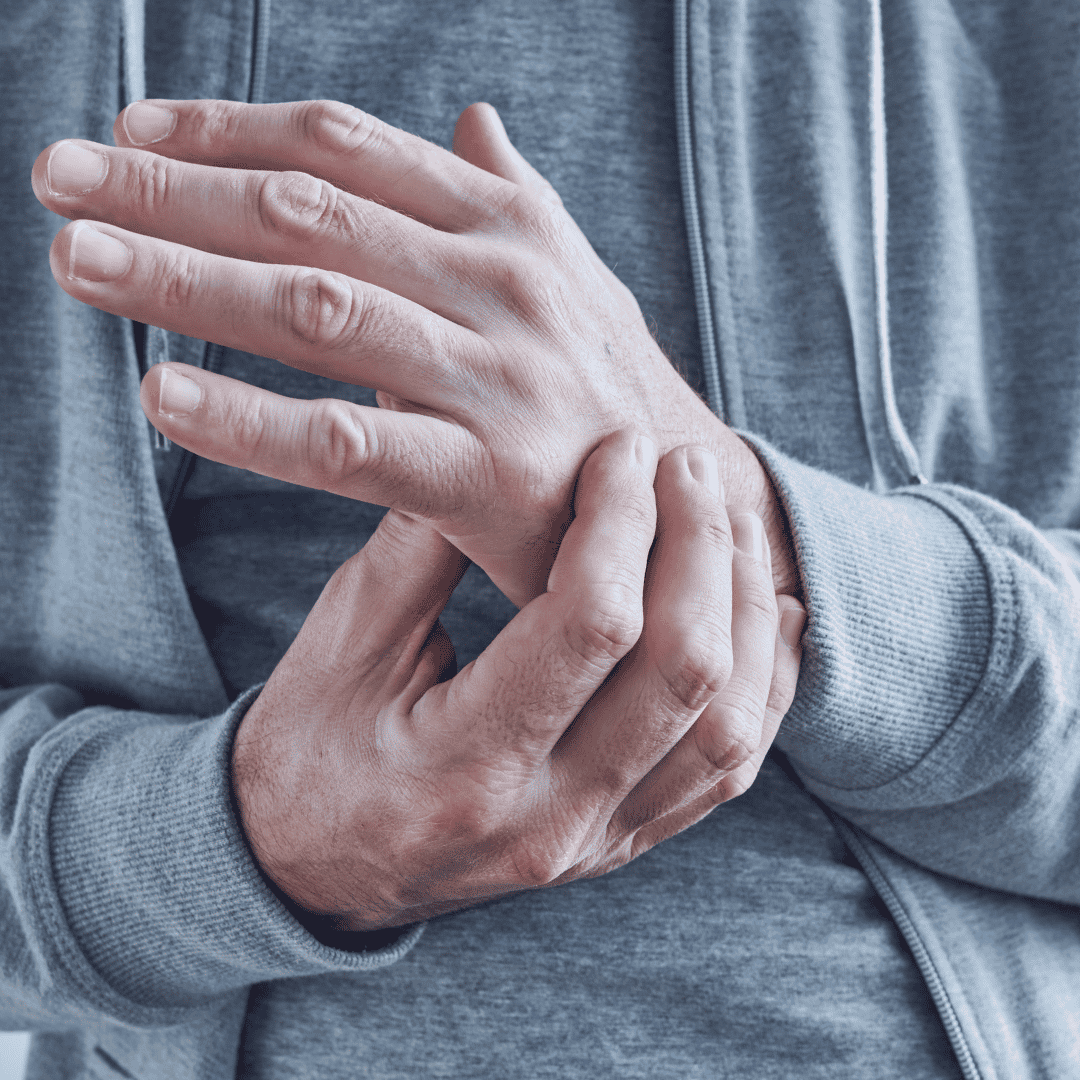
For example, many stem cell researchers today focus on treatments for auto immune disease processes such as:
- Type 1 diabetes (aka Juvenile diabetes)
- Crohn's disease
- Systemic Lupus
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Systemic vasculitis
- Multiple Sclerosis
Of course, there are dozens of other diseases stem cell research is also working on, including treatments for cancer and cardiovascular issues, vision or ocular disease processes like retinitis pigmentosa and corneal regeneration, as well as musculoskeletal disorders like muscular dystrophy.
Clinical Trials
Clinical trials of some stem cell treatments are underway in the U.S., but other countries around the world, including Mexico, Japan, South Korea and Ukraine have long been leaders in the stem cell research field.
Researchers at the National Institutes of Health in the U.S. were currently working on analyzing and comparing nearly two dozen human embryonic stem cell lines that were approved in President Bush’s administration Order and will see which ones will still be eligible in late July 2009 under Obama's Order.
Further research and development into uses of placenta and umbilical cord stem cells are already underway in many foreign research facilities, including studies and treatments for chronic disease processes, ant aging treatments, and even cosmetic and plastic surgical procedures. The potential for all types of stem cell research knows no bounds, and may very well provide hope in the future for millions afflicted with terminal diseases.
Stem Cell Process
Many different types of stem cells have the capability of developing or differentiating into specialized cells, and might be used to repair tissues destroyed from burns or traumatic injuries as well as replacing damaged cardiac cells in those who have suffered myocardial infarction, or heart attacks. Treatments for neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson's and Huntington’s disease are also in full swing.
Conclusion
Understanding the basics of stem cell function and development is the first step in educating the public with the promise of stem cell research and development. The promise of stem cells can not be denied in the 21st century, and will continue to provide untold hope for patients around the world seeking answers and cures to formerly deadly disease processes.
For More Information Click Here







.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)


.jpeg)













